The Value Of Indexable-Insert Center Drills
This indexable-insert center drill, said to be an industry first, combines the drilling performance advantages of solid carbide with the positioning repeatability and quick-change benefits common to indexable-insert tooling.
Share






Related Content
Measuring Torque, Thrust Force for Smart Drilling Operations
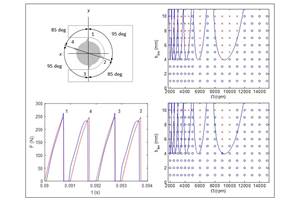
To monitor drilling operations for smart manufacturing solutions, torque and thrust force can be measured.
Read MoreHow to Mitigate Chatter to Boost Machining Rates
There are usually better solutions to chatter than just reducing the feed rate. Through vibration analysis, the chatter problem can be solved, enabling much higher metal removal rates, better quality and longer tool life.
Read MoreQuick-Change Tool Heads Reduce Setup on Swiss-Type Turning Centers
This new quick-change tooling system enables shops to get more production from their Swiss turning centers through reduced tool setup time and matches the performance of a solid tool.
Read MoreThe Impact of Cutting Teeth Spacing on Machining Stability
Many cutter designs are available, and variable teeth spacing (or variable pitch) cutters can be used to influence milling stability. Let’s discuss why teeth spacing affects stability.
Read MoreRead Next
AMRs Are Moving Into Manufacturing: 4 Considerations for Implementation
AMRs can provide a flexible, easy-to-use automation platform so long as manufacturers choose a suitable task and prepare their facilities.
Read MoreMachine Shop MBA
Making Chips and Modern Machine Shop are teaming up for a new podcast series called Machine Shop MBA—designed to help manufacturers measure their success against the industry’s best. Through the lens of the Top Shops benchmarking program, the series explores the KPIs that set high-performing shops apart, from machine utilization and first-pass yield to employee engagement and revenue per employee.
Read More